This page details how a reduced footprint as well as unidirectional data flow can be achieved when using AG Grid and VueJs.
Memory Footprint
A large part of Vue's magic comes from it's reactivity and it achieves this by observing every attribute on a component.
This is great and is what you'll want most of the time, but when it comes to large data sets - i.e. row data - it's often more performant memory wise to detach from this reactivity.
Take for example a grid that has 100,000 rows with 10 columns - the default behaviour will be that each row becomes reactive, which can become a significant memory footprint.
There are two ways in which you can detach row data from Vue's reactivity:
- Wrap your row data with
Object.freeze - Assign/Create the row data in the
createdhook
Doing either of these will ensure that Vue does not monitor the row data, which can result in a much reduced memory footprint.
Note that this is only worth considering if you have a significant amount of row data.
The trade off here is that you'll need a mechanism to update your component if the grid data changes - we'll cover that next.
Binding Row Data with v-model
You can bind row data in the usual way with :rowData="rowData", but you can also do so by using v-model.
The advantage of doing so is that this will facilitate unidirectional data flow (see next section). The main difference over normal binding is that any data changes will emit an data-model-changed event which will have the current row data as a parameter.
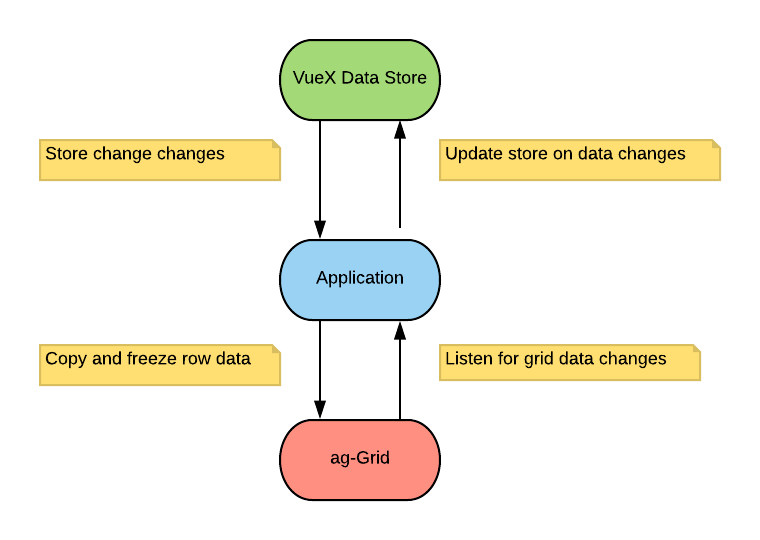
Unidirectional Data Flow / Vuex
A key tenet of Vue is the idea of unidirectional data flow - the idea that data changes flow downwards. The problem when using the grid is that the grid maintains it's own state and will modify data based on certain events (ie. if a user edits a cell).
If you pass row data down directly then both the grid and the parent component will point to the same data.
If a user edits row data then these changes are actually made on the parent components data, which breaks the unidirectional data flow.
To prevent this behaviour you should copy your data before passing it down to the grid - for example:
<ag-grid-vue
style="width: 600px; height: 150px;"
class="ag-theme-quartz"
v-model="rowData"
//..other bindings/attributes
mounted() {
const rowData = this.$store.getters.rowData; // get the data from our Vuex data store
this.rowData = Object.freeze( // reduce memory footprint - see above
rowData.map(row => { // copy to detach from the stores copy
return {
...row
}
})
)
}
By doing this the grid and component will have separate their own copies of the data. This is especially important when using something like Vuex.
Now that we've frozen and copied our data, how do we update the parent component if the grid's data changes? We'll cover this in the next section.
In the grid configuration above we made use of v-model - what this will allow us to get the row data when grid data changes:
Vue 2
<ag-grid-vue
style="width: 600px; height: 150px;"
class="ag-theme-quartz"
v-model="rowData"
@data-model-changed="dataModelChanged"
//..other bindings/attributes
methods: {
dataModelChanged(rowData) {
this.$store.dispatch('applyTransaction', rowData);
}
}
Vue 3
<ag-grid-vue
style="width: 600px; height: 150px;"
class="ag-theme-quartz"
v-model="rowData"
v-on:update:modelValue="modelChanges"
//..other bindings/attributes
methods: {
dataModelChanged(rowData) {
this.$store.dispatch('applyTransaction', rowData);
}
}
A full Vuex working example can be find in our AG Grid Vuex repo.
“$attrs is readonly”,“$listeners is readonly”,“Avoid mutating a prop directly”
Despite the wording of this warning, the issue is almost always due to multiple versions of Vue being instantiated at runtime.
This can occur in any number of ways, but the solution is simple - update (or create) webpack.config.js:
resolve: {
alias: {
'vue$': path.resolve(__dirname, 'node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js')
}
}
Here we're telling Webpack to use the full build. You may need to change the value according to the build you need.
The longer term fix is something the Vue team are contemplating - please refer to this GitHub Issue for more information.
Example Repos
The following Vue repos are available, with each demonstrating a different feature:
- Main Example
- Vuex
- i18n
- Routing
- Typescript
- UMD
- Playground: Declarative, Auto Refresh and Model Driven Examples